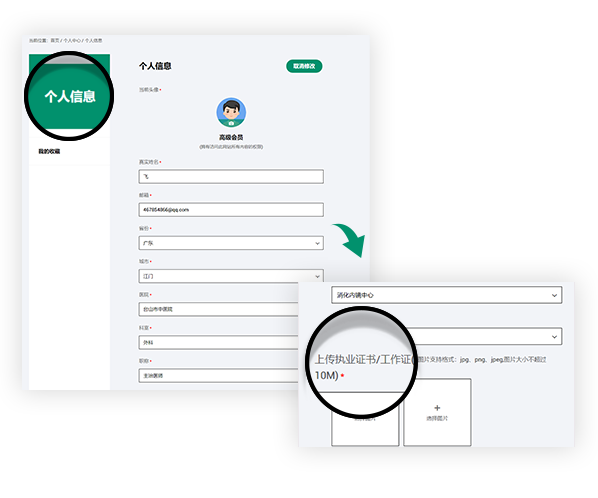
Join us you will be able to get the following rights
Get fresh academic and clinical information
Sign up for exclusive endoscopy contests and training courses
Use online training software
Watch the LIVE of academic conferences and surgery
Evaluation of the impact of linked color imaging for improving the visibility of colonic polyp
Evaluation of the impact of linked color imaging for improving the visibility of colonic polyp
Y Tanaka, T Inoue, K Kakimoto… -Oncology Letters, 2019
Abstract: Linked color imaging (LCI) is a novel endoscopic system used to increase color contrast. As LCI does not decrease luminal brightness, it may improve the detection of colonic neoplasms. However, the extent to which LCI improves the visibility of colonic polyps has not yet been determined. Between December 2016 and May 2017, patients who received total colonoscopy were consecutively recruited into this retrospective, single‑center study. For each polyp identified, images obtained from white light (WL) imaging, blue laser imaging (BLI), and LCI of the same lesion and its surrounding mucosa were evaluated. The color differences (ΔE) between each lesion and its surrounding mucosa in non‑magnified images were computed quantitatively using the CIELAB color space, which defines color perception according to colorimetric values, and compared among WL, BLI, LCI, and chromoendoscopy. The ΔE between the vessel and non‑vessel areas in magnified images was also assessed. Of the 64 patients who were incorporated into this study, non‑magnified and magnified (x80) images from 113 and 95 polyps, respectively, were assessed. The ΔE was intensified by LCI and chromoendoscopy compared with WL and BLI. The ΔE of neoplastic lesions was also intensified by LCI. In magnified images, BLI and LCI significantly increased the ΔE between the vessel and non‑vessel areas compared with WL. Luminal brightness, indicated by L*, was not impaired by LCI; however, was reduced by BLI compared with WL and LCI. These results suggest that LCI enhanced the detection of colonic neoplasms without impairing luminal brightness. We propose the routine use of LCI for colonic polyp detection and BLI for magnifying observations of colonic polyps detected by LCI.
声明
富士胶片内镜世界(LIFE World)所登载的内容及其版权和使用权归作者本人与富士胶片所有。如发现会员擅自复制、更改、公开发表或其他以盈利为目的的使用,富士胶片将追究其法律责任。网站信息中涉及的治疗手技皆为术者个人针对该名患者特定体质及健康状况所采取的手法;术者对器械和药品种类的选择,也受到手术发生时间、地点等诸多因素的影响。因而相关内容及信息仅供会员参考。如盲目使用网站信息中涉及的治疗手技而发生意外,恕富士胶片及本网站对此不承担任何责任。